Luminous Efficacy and Useful Lumens: A Comprehensive Guide to Efficient Lighting Design
- By Ledrise Led Professional
- Feb 10, 2023

Luminous efficacy measures how effectively a light source produces visible light. It is a critical parameter when considering the energy efficiency and performance of light sources, especially for LED lighting. In this article, we will delve deeper into the concept of luminous efficacy, useful lumens, and how to choose the right lighting solutions for your projects to achieve optimal energy efficiency and lighting design.
Understanding Luminous Efficacy
Luminous efficacy is the ratio of luminous flux (the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source) to electrical power consumption, expressed in lumens per watt (lm/w). A higher luminous efficacy indicates a more efficient light source, as it produces more visible light with less power consumption.

LED Performance and Luminous Efficacy
The luminous efficacy of LEDs varies greatly, depending on their performance and manufacturing quality. Here's a quick overview of the different categories of LED performance based on their luminous efficacy:
| Top performance LED | High Performance LED | Good Performance LED | Poor Performance LED |
| 220 lm/W | 150-200 lm/W | 100-149 lm/W | 50-99 lm/W |
- Top Performance LEDs: These LEDs have the highest luminous efficacy, around 220 lm/w. Examples include the Nichia 757G LEDs.
- High Performance LEDs: These LEDs offer good performance with a luminous efficacy of 150-200 lm/w. Many reputable manufacturers produce LEDs in this category.
- Good Performance LEDs: These LEDs have a moderate luminous efficacy of 100-149 lm/w, suitable for general applications.
- Poor Performance LEDs: These low-cost, low-quality LEDs have a luminous efficacy of less than 99 lm/w, and are often not recommended for energy-efficient lighting solutions.
The other light sources on the market today have luminous efficacy:
| Category | Type | Overall luminous efficacy (lm/W) |
|---|---|---|
| Incandescent | 15, 40, 100 W tungsten incandescent (230 V) | 8, 10, 13 |
| 5, 40, 100 W tungsten incandescent (120 V) | 5, 12, 17 | |
| Halogen incandescent | 100, 200, 500 W tungsten halogen (230 V) | 16, 17, 19 |
| 2.6 W tungsten halogen (5.2 V) | 19 | |
| Halogen-IR (120 V) | 17–24 | |
| Tungsten quartz halogen (12–24 V) | 24 | |
| Photographic and projection lamps | 35 | |
| Arc lamp | Carbon arc lamp | 2–7 |
| Xenon arc lamp | 30–50 | |
| Mercury-xenon arc lamp | 50–55 | |
| Ultra-high-pressure (UHP) mercury-vapor arc lamp, free mounted | 58–78 | |
| Fluorescent | 32 W T12 tube with magnetic ballast | 60 |
| 9–32 W compact fluorescent (with ballast) | 46–75 | |
| T8 tube with electronic ballast | 80–100 | |
| PL-S 11 W U-tube, excluding ballast loss | 82 | |
| T5 tube | 70–104 | |
| Gas discharge | 1400 W sulfur lamp | 100 |
| Metal halide lamp | 65–115 | |
| High-pressure sodium lamp | 85–150 | |
| Low-pressure sodium lamp | 100–200 |
Considering Illuminance and Beam Angle
When designing an energy-efficient lighting system, it's essential to consider not just the luminous efficacy of the light source, but also how effectively the light output is transferred to the desired area. The illuminance (the amount of light falling on a surface) is determined by the luminaire design and the viewing angle (beam angle) of the light source.
The same light source can have different illuminance values when used in different mounts or with varying beam angles. With the same power consumption, you can have insufficient, optimal, or overly bright lighting in some areas, depending on the luminaire design and beam angle.
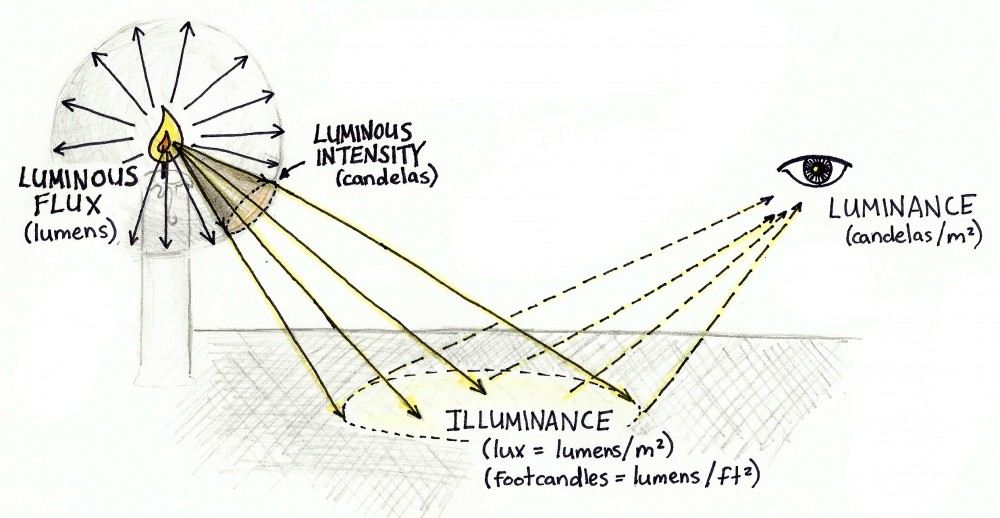
Understanding Useful Lumens
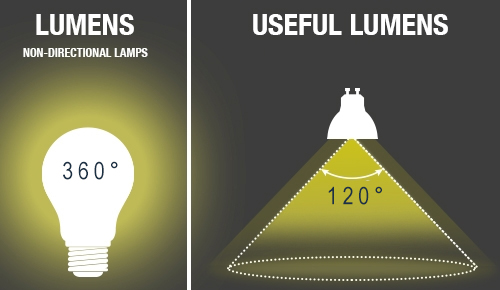
Useful lumens refer to the amount of light emitted by a light source that is directed towards the intended area, which contributes to the actual illuminance. Non-directional light sources, such as traditional light bulbs with a 360° beam angle, often have a low useful lumens value, as much of the light is emitted in other directions, leading to wasted energy and suboptimal lighting.
By using a light source with a focused beam, such as an LED strip with a 120° viewing angle or an LED spotlight with a 60° or narrower beam angle, you can achieve higher illuminance on the intended surface with lower power consumption and total lumen output. In other words, a lower power light source with focused light can have more "useful lumens" than a high power bulb that emits light omnidirectionally.
Comparing useful lumens of different light fixtures is recommended when choosing the most suitable and energy-efficient lighting solutions for your projects.
Choosing the Right LED Lighting Solutions
When selecting LED lighting solutions, it's crucial to consider the following factors to achieve the best energy efficiency and lighting performance:
- Luminous efficacy: Opt for high-performance LEDs with high luminous efficacy to minimize energy consumption and maximize light output.
- Beam angle: Choose light sources with appropriate beam angles to direct light effectively towards the intended area and maximize useful lumens.
- Luminaire design: Select well-designed luminaires that efficiently transfer light output to the desired surface, ensuring optimal illuminance levels.
- Color rendering index (CRI): High CRI LEDs can reproduce colors more accurately, improving the overall quality of lighting and creating a more visually appealing space.
- Lifespan and reliability: Choose LEDs from reputable manufacturers to ensure a long lifespan and consistent performance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
- Warranty and support: Opt for LED lighting solutions backed by solid warranties and reliable customer support to safeguard your investment and address any potential issues that may arise.
Understanding the concepts of luminous efficacy and useful lumens is crucial for designing energy-efficient and effective lighting systems. By considering factors such as LED performance, beam angle, and luminaire design, you can optimize your lighting solutions to maximize useful lumens and achieve the desired illuminance levels while minimizing energy consumption.
At Ledrise, we offer a wide range of LED strips and modules that deliver the highest useful lumens. Our products feature directed beam angles and utilize some of the most efficient LEDs on the market. By choosing Ledrise for your LED lighting needs, you can be confident in the quality, performance, and energy efficiency of your lighting solutions.



























